What Is Web3 Innovation?
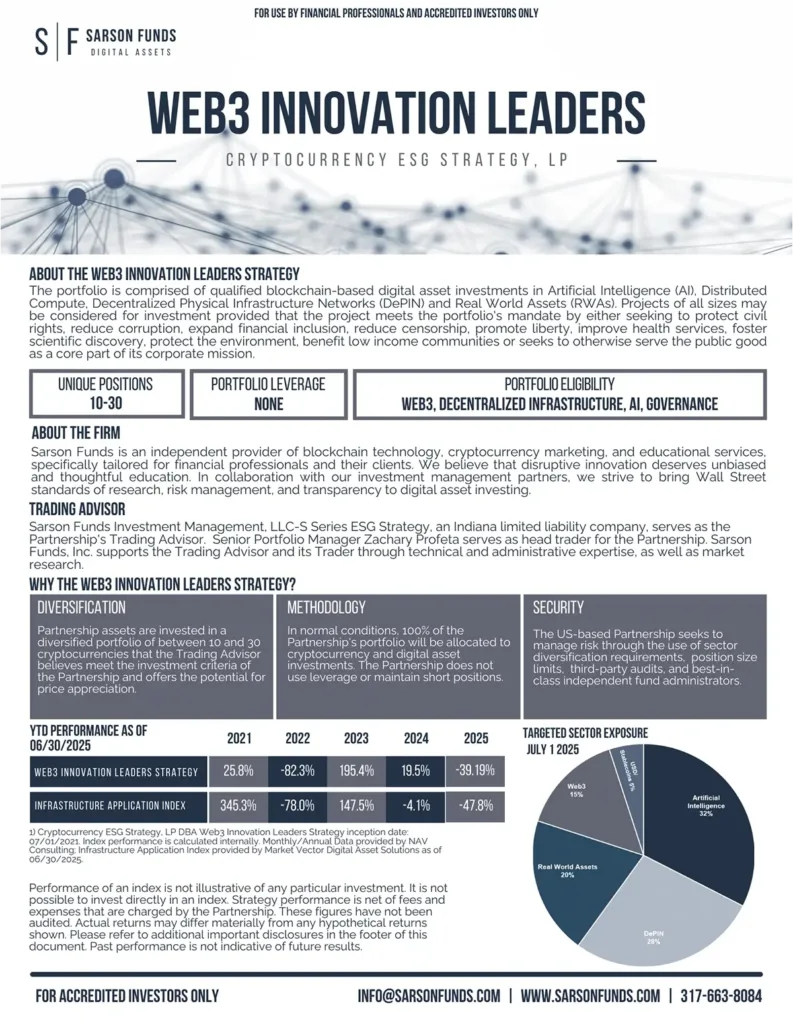
WEB3 INNOVATION LEADERS (Cryptocurrency ESG Strategy, LP) strategy is comprised of qualified blockchain-based digital assets investments in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Distributed Compute, Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) and Real World Assets (RWAs). Projects of all sizes may be considered for investment provided that the project meets the portfolio’s mandate by either seeking to protect civil rights, reduce corruption, expand financial inclusion, reduce censorship, promote liberty, improve health services, foster scientific discovery, protect the environment, benefit low income communities or seeks to otherwise serve the public good as a core part of its corporate mission.
Strategy Overview
Investment Process
Meet Discretionary Standards
Web3 Innovation Leaders strategy is committed to meeting discretionary standards that prioritize Artificial Intelligence (AI), Distributed Compute, Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) and Real World Assets (RWAs). By incorporating these principles into our investment process, we aim to deliver strong returns while promoting sustainable development and responsible investing practices
DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks)
We believe that cryptocurrencies can play a critical role in creating public goods that benefit society as a whole. Our strategy focuses on supporting projects and initiatives that promote financial inclusion, transparency, and accessibility, ultimately contributing to the greater good. Public goods are non-excludable, non-rivalrous utilities and services that provide benefit to the public.
Scaling and Interoperability
As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, we recognize the importance of scaling and interoperability in achieving mainstream adoption. Our investment approach prioritizes projects that demonstrate scalability, interoperability, and a clear roadmap for growth, ultimately driving the industry forward. This includes protocols implemented to improve the feature set of high-traffic Layer 1 networks, enabling fee reduction, energy cost/tax reduction, or higher throughput computing environments.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Our strategy includes investing in projects that leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance the capabilities and efficiency of blockchain technologies. AI can drive innovation in various areas such as automated decision-making, predictive analytics, and intelligent contract execution. By prioritizing AI-driven projects, we aim to push the boundaries of what is possible within the Web3 ecosystem and ensure our investments remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
Censorship-Resistant Protocols and Blockchains
We prioritize investments in protocols and blockchains that are designed to be censorship-resistant, ensuring that data and transactions remain secure, immutable, and accessible. These technologies are crucial for maintaining the integrity and decentralization of the Web3 ecosystem. By supporting censorship-resistant solutions, we aim to protect user freedoms, promote open access, data sovereignty, and foster innovation in a truly decentralized manner.
Monthly Liquidity After 90 Days
We recognize the importance of liquidity for all our clients. Although our strategies generally involve holding positions for longer durations, we offer regular liquidity events to provide access to capital. Following an initial 90-day lock-up period, we ensure monthly liquidity to grant our clients the flexibility they require.
Click the FactCard below to download
Book an Info Session
Book a digital asset discovery session to learn more about this strategy, or other strategies offered by Sarson Funds.
Request Information
Submit this request form to receive investor information.


Real World Assets (RWAs)
Our investment strategy focuses on integrating Real World Assets (RWAs) into blockchain ecosystems. This involves tokenizing traditional financial instruments like real estate, commodities, bonds, and securities. These tokenized assets provide increased liquidity, transparency, and accessibility, transforming traditional asset management and trading. By investing in projects that enable the seamless integration of RWAs, we aim to unlock new opportunities for capital efficiency and financial inclusion.